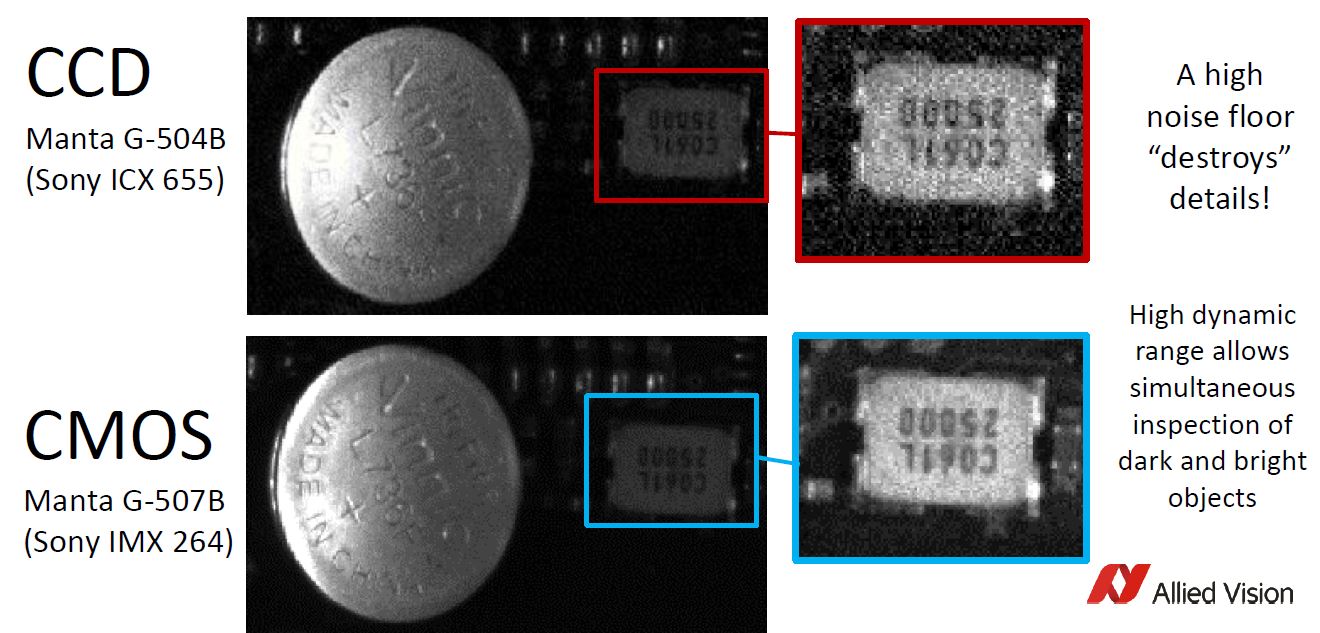
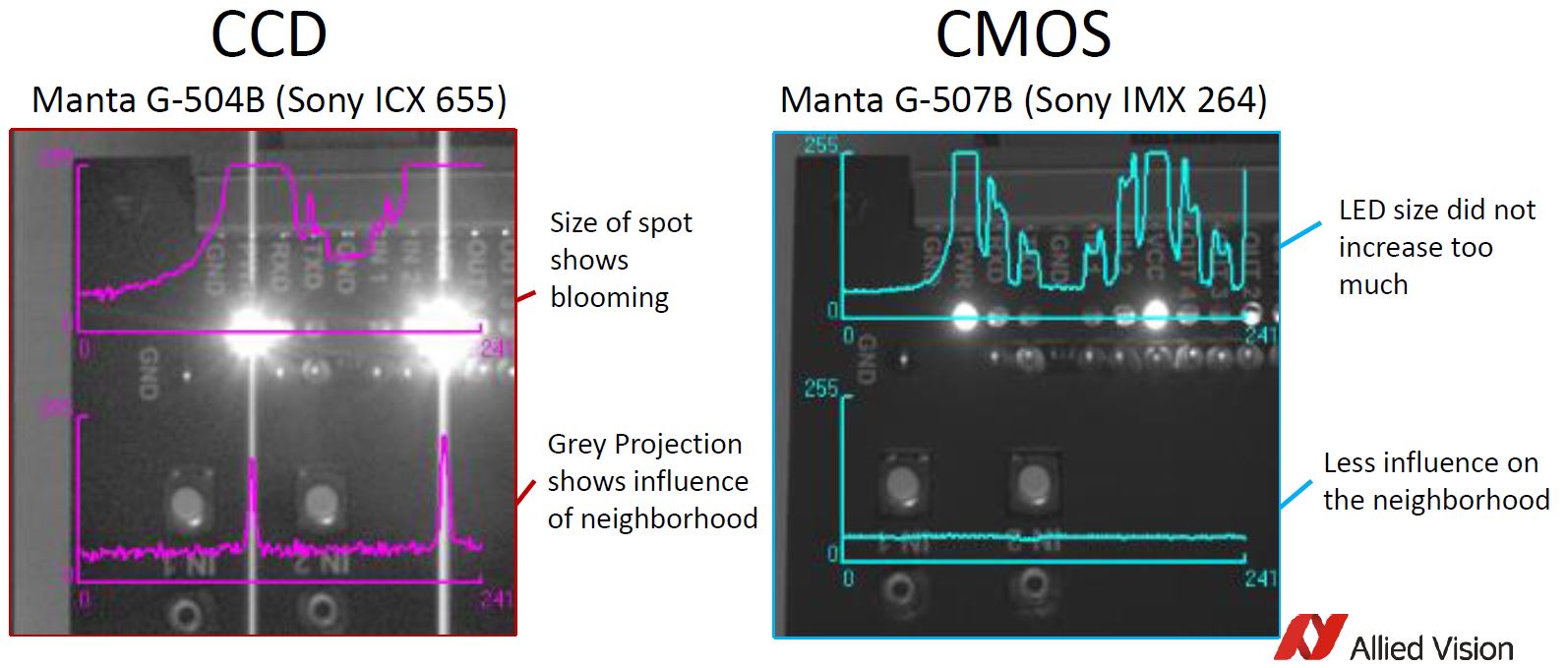
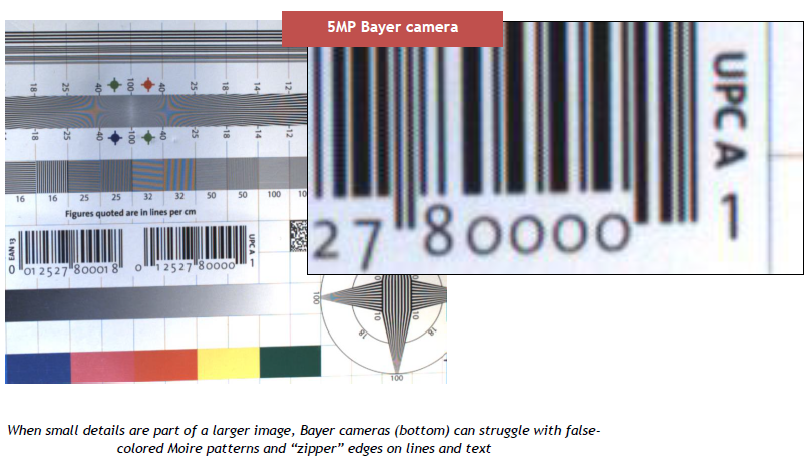
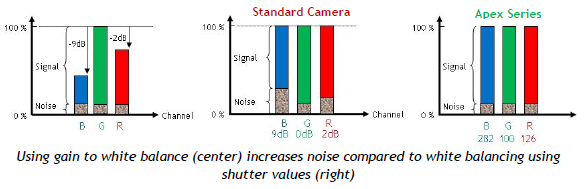
Machine vision interfaces have continued to evolve over the years increasing data throughput and cable lengths. Commonly used interfaces are GigE and USB3. However, 5GigE is an interface now gaining attention in the industrial imaging / machine vision market with some nice advantages.
Machine vision interfaces have continued to evolve over the years increasing data throughput and cable lengths. Commonly used interfaces are GigE and USB3. However, 5GigE is an interface now gaining attention in the industrial imaging / machine vision market with some nice advantages.
We will outline the benefits of 5GigE, but first, lets give a brief overview of the commonly used camera interfaces, with their pluses and minuses:
GigE / GigE Vision
- 110 MB/s of sustainable throughput. In real world terms, a HD, 2MP camera can get 50-55 fps in 8 bit mono or 8 bit color mode. Note, this isn’t real HD, since you need 60 FPS.
- Data cable lengths up to 100m using regular CAT 5e/6 cable.
- Easy to put multiple cameras on a system.
USB 3 / USB3 Vision
- 420 MB/s of data throughput. A HD 2MP camera can run 60 fps in 8 bit mono or color and can also run RGB at 60 FPS no problem. With the higher throughput, a 5MP camera can achieve 85 fps in 8 bit mode.
- Data cables up to 5 meters and up to 20 meters with active cables. However, active cables can be quite costly, adding up to $200 in cost.
- Not as easy as GigE to put multiple cameras on a system, and gets harder with each additional camera, especially if you have limited USB3 controllers.
As a note, there is no cost difference when using cameras with the same sensor from the same manufacturer with USB or GigE! They will cost about the same with no premium for one interface over the other.
 What are the limitations of GigE and USB3 now solved by 5GigE?
What are the limitations of GigE and USB3 now solved by 5GigE?
- USB3 is limited in cable length, so going faster than GigE is great, but you can not have long cable lengths.
- GigE has cable lengths up to 100 meters, but is limited to ~ 110MB/s of data, so you do not have the high frame rates as in a USB3 camera.
- USB3 in 4+ camera systems is not as stable as GigE AND you’re still limited on cable lengths.
Wait! – What about 10GigE?
Up until now, 10G was the next interface. However, the jump to 10G has quite a few limitations as outlined below.
- Heat generation is significant, so cameras are large and not in the smaller 29 x 29mm cube form factor.
- Not a lot of demand for very high speed 10G, so not a lot of sensors being offered
- Minimal number of manufacturers for 10G, higher cost.
- Special cabling, either optical or high quality cat 7.
What we have found is that there are several types of applications for 10G cameras and are as follows
- Applications where you need 10G of speed of course (high resolution + fast frame rates)
- Require greater than 110MB/s of data and need long cable lengths.
- Where there is the required combination of 110MB/s for high frame rates, multiple cameras and long cable lengths, 10G is a perfect solution.
We have seen that the need for higher bandwidth + long cable lengths is more prominent vs. the real need for 10GigE!
Introducing 5GigE that provides increased bandwidth, long cable lengths at reasonable prices! or N Base T.
5GigE (also known as N Base T) has become a new standard for industrial, machine vision cameras.
In the general compute world, a much much larger market than vision, there has also been a need to go faster than GigE. However, the issue of replacing the existing cabling is the major issue preventing this. If you think of a big box store, say a Home Depot for instance, the amount of cabling is huge. Ripping that out and rewiring far exceeds the cost of the equipment to use it!
5G was made to go faster, but use existing cabling. Regular cat6e cable can be used, and 5G is a subset of 10G, so all switches etc. can be kept in service.
5G gives users in the vision market USB3 speeds, but with ALL of the regular GigE features, at a very small premium!
 1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC card and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC card and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!