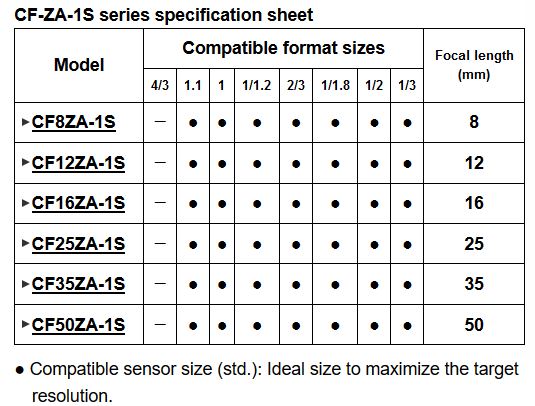
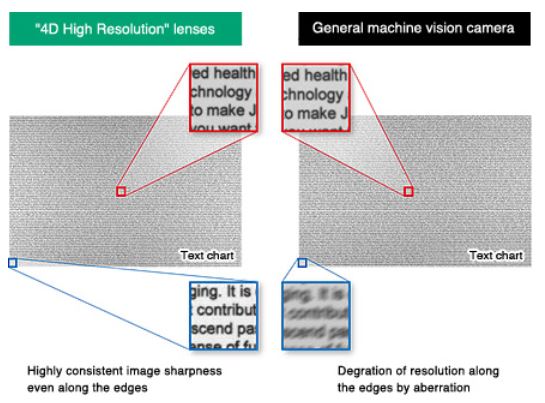
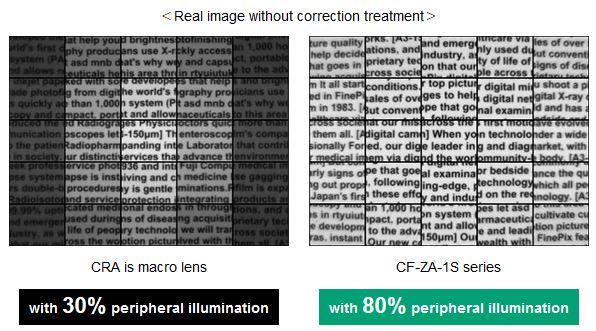
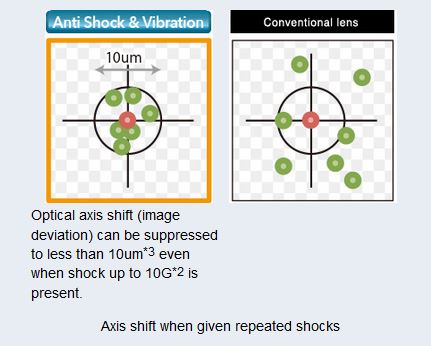
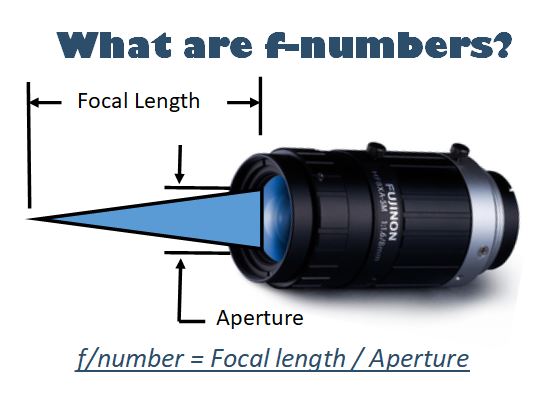
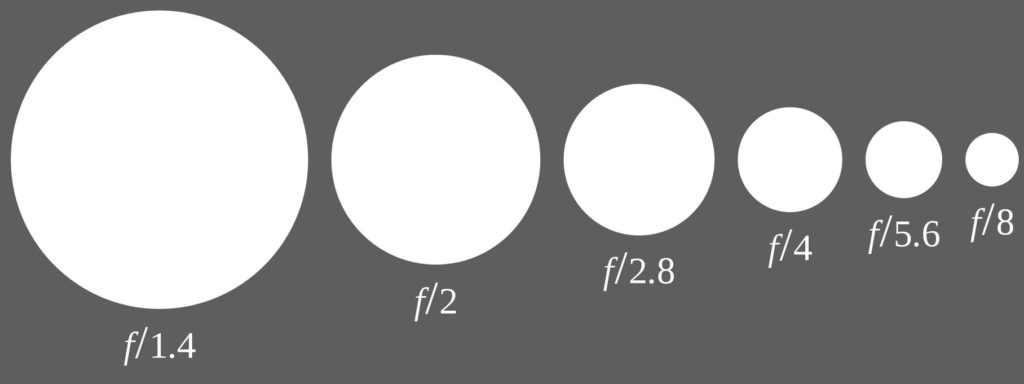
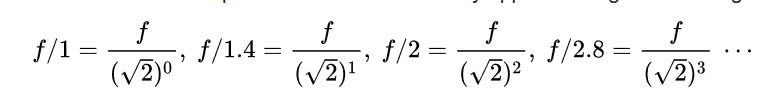Liquid lens technology, with its ability to change focus within the order of milliseconds is opening up a host of new applications in both machine vision and the life sciences. It is gaining growing interest from a wide cross section of applications and easily adapts to standard machine vision lenses.
Liquid lens technology, with its ability to change focus within the order of milliseconds is opening up a host of new applications in both machine vision and the life sciences. It is gaining growing interest from a wide cross section of applications and easily adapts to standard machine vision lenses.
Liquid lens technology alone provides nice solutions, but when combined with advanced controls, many more applications can be solved.
In this blog, we will highlight several case application areas for liquid lens technology.
Case 1: Applications requiring various focus points and extended depth of field: This does cover many applications, such as logistics, packaging and code reading in packaging. Optotune Liquid lenses provide the ability to have pre-set focus points, auto-focus or utilize distance sensors for feedback to the lens. In the example below, 2 presets can be programmed and toggled to read 2D codes at various heights essentially extending the depth of field.
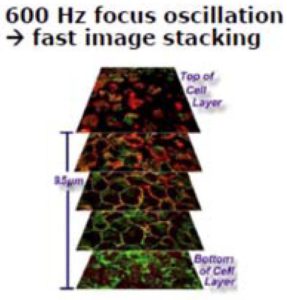
Case 2: 3D imagery of transparent materials / Hyperfocal (Extended DOF Images: When 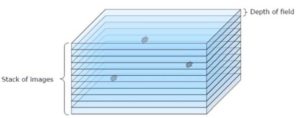 using an Optotune liquid lens in conjunction with a Gardasoft TR-CL180 controller, sequence of images can be taken with the focus point stepped between each image. This technique is known as focus stacking. This will build up a 3D image of transparent environments such as cell tissue or liquid for analysis. This can also be used to find particles suspended in liquids.
using an Optotune liquid lens in conjunction with a Gardasoft TR-CL180 controller, sequence of images can be taken with the focus point stepped between each image. This technique is known as focus stacking. This will build up a 3D image of transparent environments such as cell tissue or liquid for analysis. This can also be used to find particles suspended in liquids.
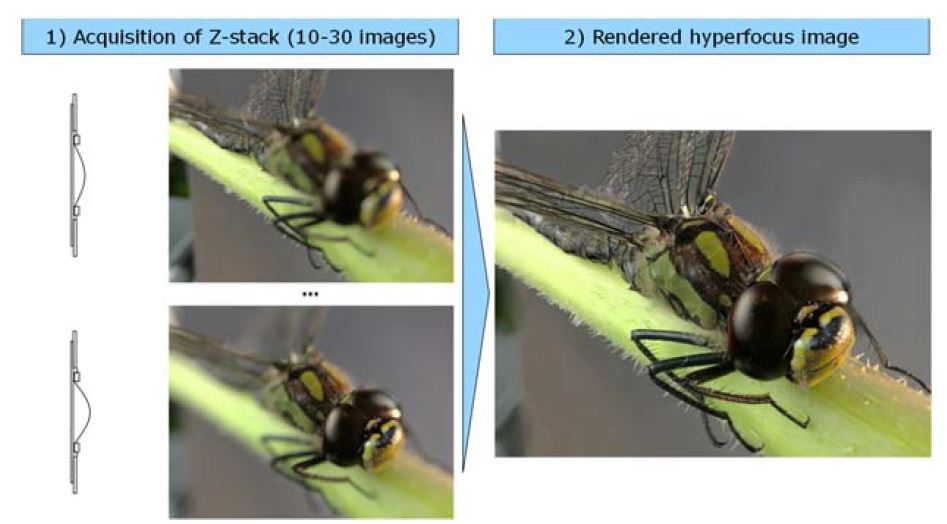
A Z-stack of images can also be used to extract 3D data (depth of focus) and compute a hyper-focus or extended depth of field (EFOF) image.
The EDOF technique requires tacking a stack of individual well focused images which have preferably been synchronized with one flash per image. An example is show below with the rendered hyper focus image shown at right.
 Case 3: Lens inspection: Liquid lenses can be used to inspect lenses, such as those in cell phones for dust and scratches looking through the lens stack.
Case 3: Lens inspection: Liquid lenses can be used to inspect lenses, such as those in cell phones for dust and scratches looking through the lens stack.
Case 4: Bottle / Container inspection: Optotune Liquid lenses can be used to facilitate image bottom’s of glass bottles or containers of various heights.
In this example, the camera is consistently at the neck of the bottle, but the bottom is at different heights.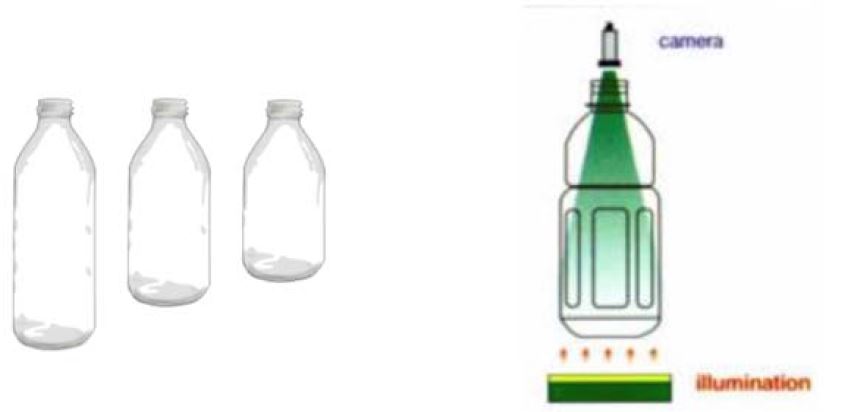 
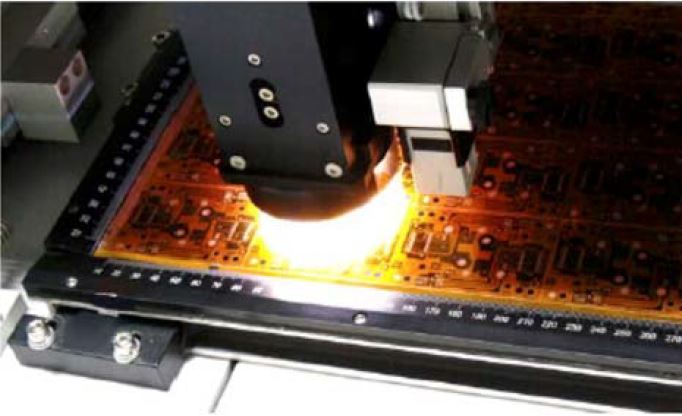
Case 5: Large surface inspections with variation in height: Items ranging from PCB’s to LCD’s are not flat, have various component heights and need to be inspected at high magnification (typically using lenses with minimal DOF). Optotune Liquid lenses are a perfect solution using preset focus points.
Machine Vision applications using Optotune Liquid lenses and controller are endless!
These applications are just the tip of the iceberg and many more exist, but this will give you a good idea of capabilities. Gardasoft TR-CL controllers are fully GigE Vision compliant, so any compatible GigE Vision client image processing software such as Cognex VisionPro, Teledyne Dalsa Sherlock or National Instruments LABVIEW can be used easily.
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC card and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!
Contact us to help in the specification and providing pricing
Ph: 978-474-0044 / info@1stvision.com / www.1stvision.com
Related Video
Related Blog Posts



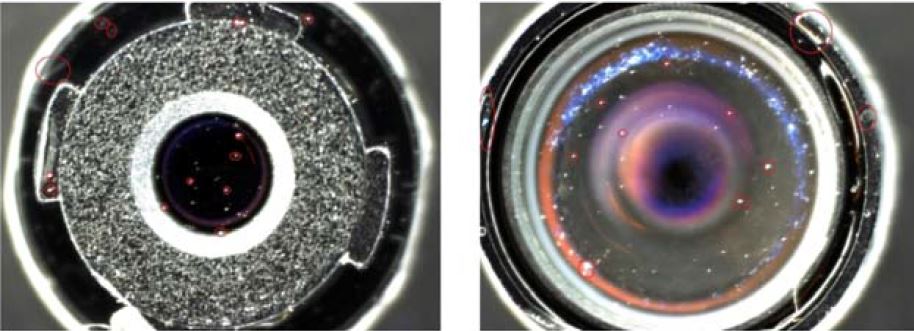 For this application, a liquid lens is used in conjunction with a telescentric lens taking images through different heights of the lens stack.
For this application, a liquid lens is used in conjunction with a telescentric lens taking images through different heights of the lens stack.